- A +
- A
- A -
Application and development of 3D scanners
With the development of computer technology in recent years, all walks of life continue to pursue innovation. Primitive industrial manufacturing, film and television production, clothing design, aviation, medical diagnosis and other industries have gradually put forward increasingly urgent needs: to quickly obtain three-dimensional models of objects.

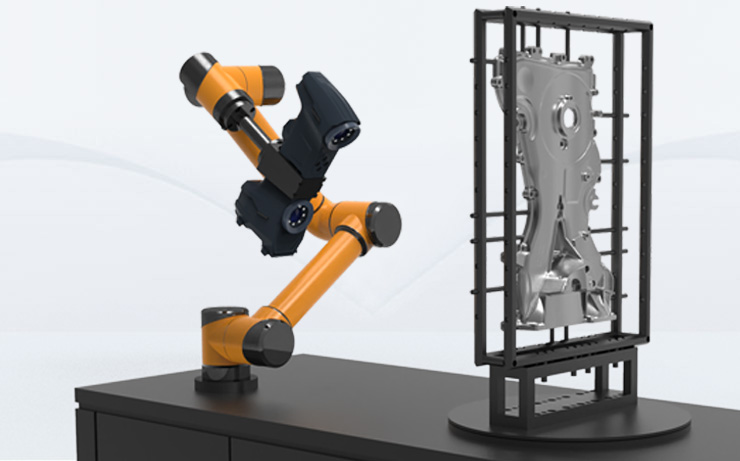
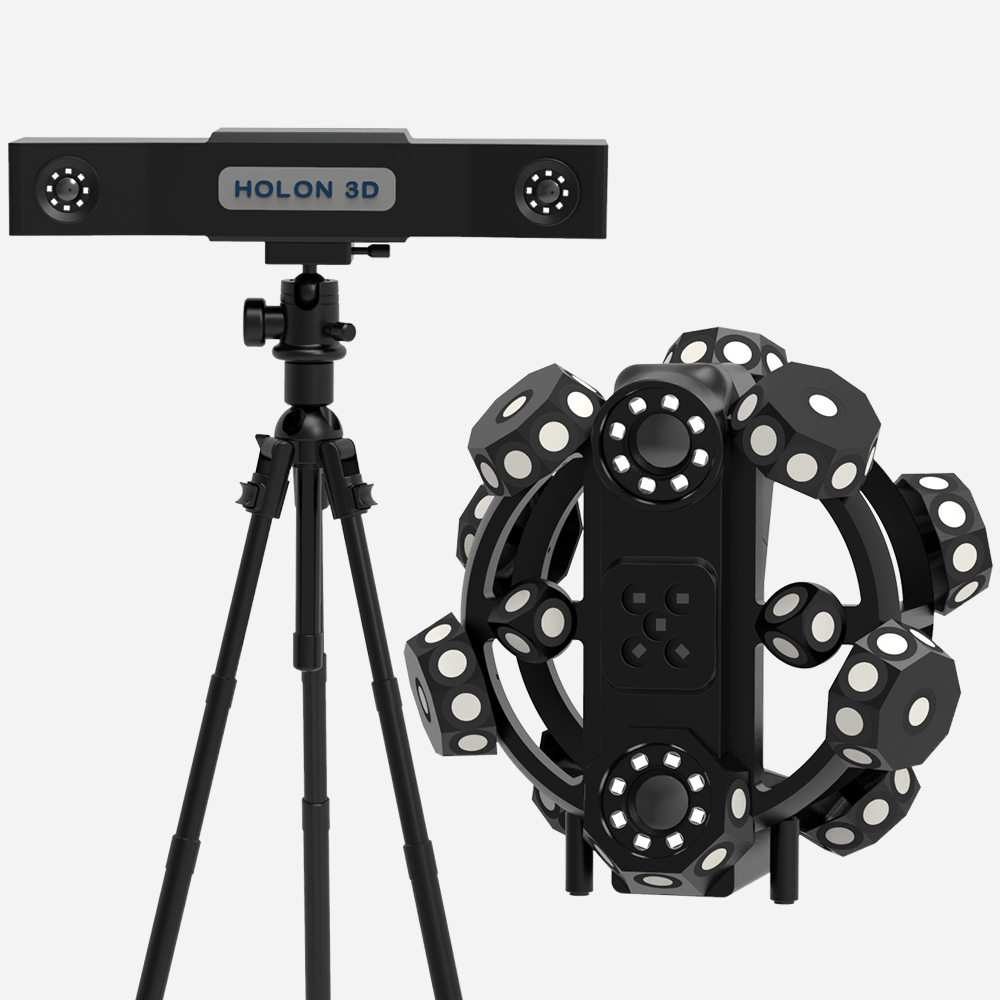
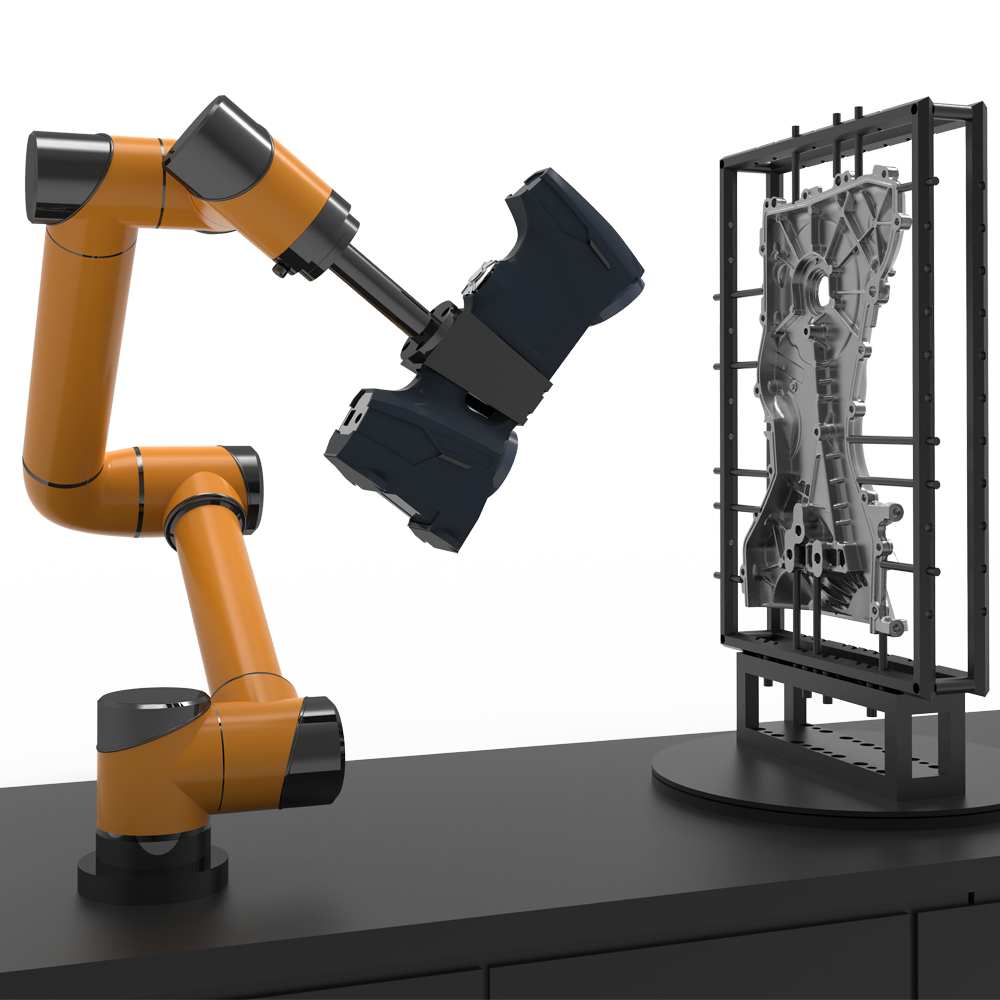
As a computer input device that uses a combination of optical, mechanical, and electrical technologies to directly obtain the original three-dimensional information of an object, the 3D scanner is becoming a key tool to meet this demand. The technology of obtaining product mathematical models from physical samples, that is, reverse engineering, also plays an important role in this process.
At first, reverse engineering was only used for virtual reconstruction of objects, but with the gradual development of 3D printers, its application scope has been extended to the reconstruction of objects in real life. Therefore, the application of 3D scanners is becoming increasingly widespread.
Classification and Application of 3D Scanners
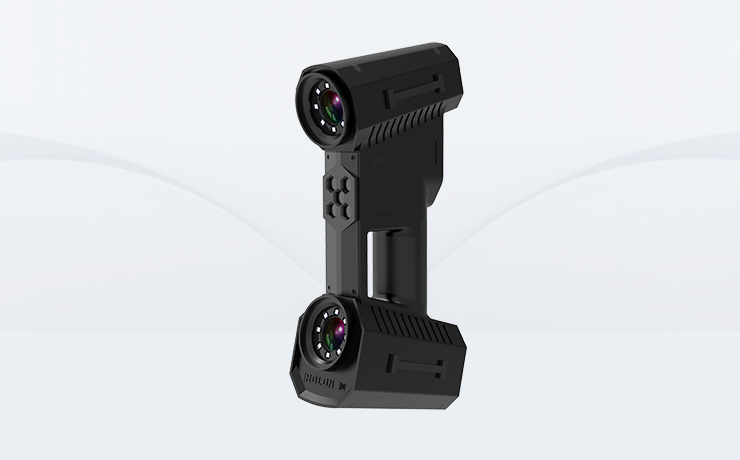
Generally speaking, 3D scanners can be divided into two types: contact and non-contact. Common raster scanners such as white light scanning and blue light scanning, and laser scanners such as point laser scanning, line laser scanning, and surface laser scanning all belong to the category of non-contact 3D scanners. Three-dimensional scanners built with different technologies also have different application ranges.
Due to the strong penetrability of laser technology, laser 3D scanners are not suitable for objects with fragile surfaces and easy to change; while optical technology is difficult to handle shiny surfaces, making grating 3D scanners not suitable for objects with mirror surfaces. .
Accuracy and data processing of 3D scanners
System structural parameter deviations will lead to coordinate measurement errors. In order to improve the measurement accuracy, it is very necessary to calibrate the 3D scanner to obtain the actual structural parameters as accurately as possible.
During the scanning process of objects with a 3D scanner, due to limitations of various factors, the data obtained from some parts of the object may be incomplete, resulting in incomplete 3D data. Therefore, the measurement data need to be extended and repaired.
3D reconstruction technology
After obtaining the "point cloud" data of the object surface sampling points, the model must be described in the form of polygons, curves, surfaces, etc., that is, three-dimensional reconstruction. As a three-dimensional reconstruction method, the triangular mesh model was studied for triangulation of regular data and scattered data respectively.
For the regular data obtained by structured light scanning, a heuristic search algorithm based on contour line correlation is proposed. For the scattered data obtained by multi-joint scanning, the cross-sectional contours are first cut, and then the cross-sections are sorted. Construct a triangular mesh between two ordered sections.